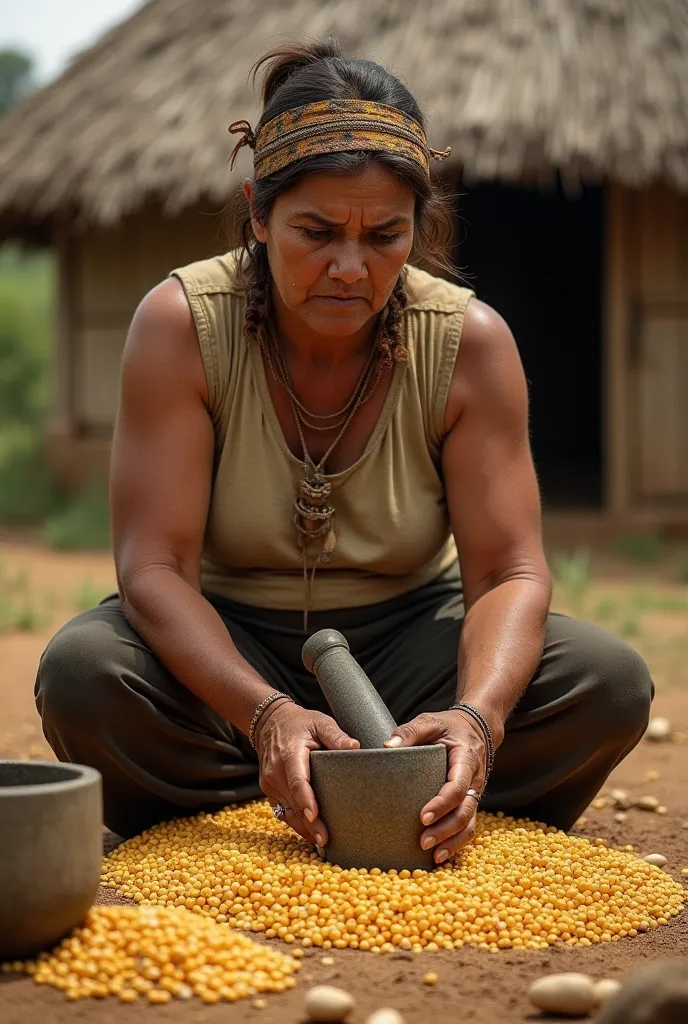
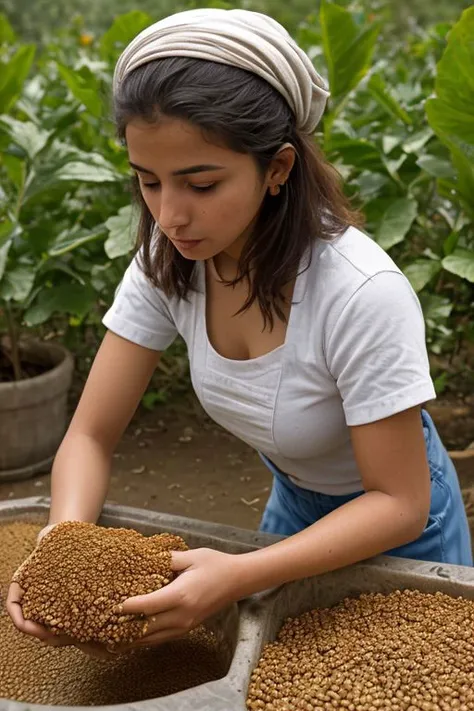
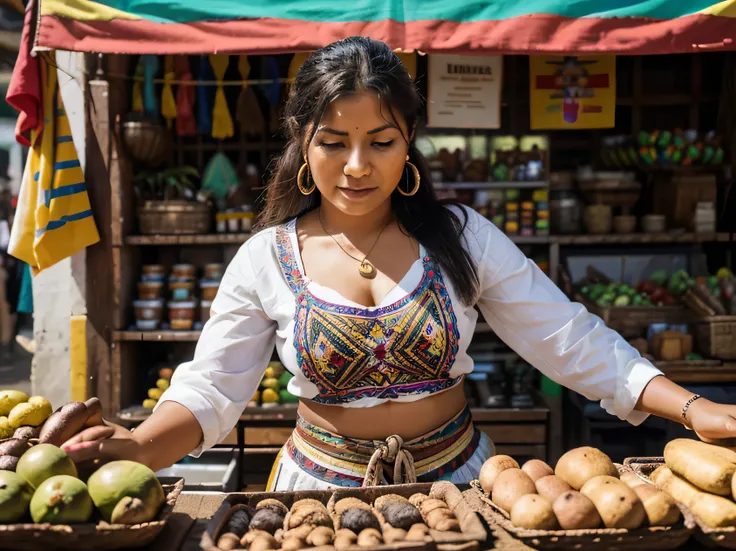
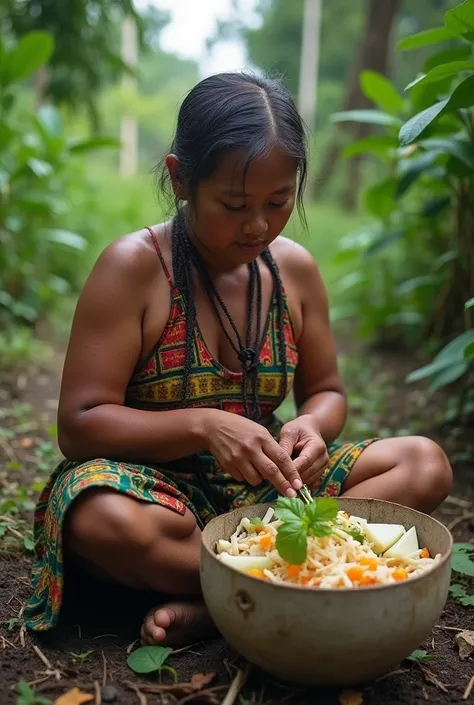
Woman in traditional dress preparing food in outdoor setting


La Influencia Inca en la Cocina de la Hoya de Guayllabamba En los siglos XV y XVI, The cuisine of the Guayllabamba basin experienced a notable Inca influence, with the introduction of new products, culinary artifacts and techniques. Los incas, initially led by Tupac Yupanqui and later consolidated by his son Huayna Cápac, They implemented a system of conquest that included the relocation of populations, conocido como mitma, to ensure agricultural control and development, military and irrigation engineering in the region. Resistencia y Conquista Resistencia del Norte: While the ethnic lordships of the south allied themselves with the Incas, los del norte resistieron, construyendo pucaras (fortalezas defensivas) en San Antonio de Pichincha, El Quinche y Quitopamba. Domain Consolidation: Huayna Cápac consolidated the Inca conquest in the region by defeating the Caras in Cochasquí, evento conocido como la batalla de Yahuarcocha o "lago de sangre". Relocation of Populations (Mitma) Strategic Mobilization: Los incas trasladaron a los cayambis a Ancasmarca, cerca del lago Titicaca, and replaced them with Collao natives. Groups of Cañaris and Chachapoyas were located near Cotocollao, mientras que en Uyumbicho y Achambo se instalaron familias de la etnia huayacuntu, originarias del oriente de Piura. Experiencia y Estrategia: The relocations considered the agricultural and military skills of the populations, placing irrigation experts in dry areas like Pomasqui and soldiers in resistance zones like El Quinche.
Prompts
Copiar prompts
La Influencia Inca en la Cocina de la Hoya de Guayllabamba
En los siglos XV y XVI
,
The cuisine of the Guayllabamba basin experienced a notable Inca influence
,
with the introduction of new products
,
culinary artifacts and techniques
.
Los incas
,
initially led by Tupac Yupanqui and later consolidated by his son Huayna Cápac
,
They implemented a system of conquest that included the relocation of populations
,
conocido como mitma
,
to ensure agricultural control and development
,
military and irrigation engineering in the region
.
Resistencia y Conquista
Resistencia del Norte: While the ethnic lordships of the south allied themselves with the Incas
,
los del norte resistieron
,
construyendo pucaras (fortalezas defensivas) en San Antonio de Pichincha
,
El Quinche y Quitopamba
.
Domain Consolidation: Huayna Cápac consolidated the Inca conquest in the region by defeating the Caras in Cochasquí
,
evento conocido como la batalla de Yahuarcocha o "lago de sangre"
.
Relocation of Populations (Mitma)
Strategic Mobilization: Los incas trasladaron a los cayambis a Ancasmarca
,
cerca del lago Titicaca
,
and replaced them with Collao natives
.
Groups of Cañaris and Chachapoyas were located near Cotocollao
,
mientras que en Uyumbicho y Achambo se instalaron familias de la etnia huayacuntu
,
originarias del oriente de Piura
.
Experiencia y Estrategia: The relocations considered the agricultural and military skills of the populations
,
placing irrigation experts in dry areas like Pomasqui and soldiers in resistance zones like El Quinche
.
INFO
Checkpoint & LoRA

Checkpoint
epiCRealism
#Realista
#Fotografia
comentário(s)
0
0
0